Server Virtualization - Why You Should Use It and the Best Software Solutions
One of the most important reasons for Server Virtualization in IT organizations is the wish for better utilization. Servers of the current generation often only use 10-20% of their capacity. Nevertheless, in many industries, it is necessary to keep certain applications separate from each other. This also makes it easier to monitor and manage server resources.

Here you'll find Server Virtualization
Do you need help?
Simply call us or use our inquiry form.
What Is Server Virtualization?
Server virtualization is used to provide systems, applications, or server resources in a virtualized form. With a “virtual server,” the system can operate in the same way as it would with a physical server.
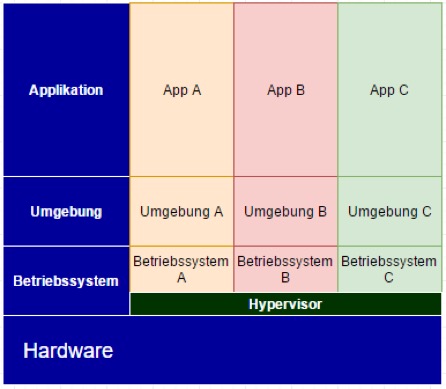
Each virtual machine (VM) runs its own operating system, while the underlying server hardware is shared. This creates independent environments that can be configured individually to meet different requirements. Virtual machines are also referred to as logical partitions, logical domains, or kernel-based virtual machines (KVM).
What are the advantages of server virtualization?
Companies can use server virtualization in a variety of ways to leverage their resources more efficiently and save money in the long run:
- Fully utilized hardware resources
- Easy configuration
- Efficient allocation of resources
- More space and lower electricity needs
- Free choice of servers for virtualization
- New space for old applications
Server Virtualization: The Three Most Common Virtualization Approaches
To implement server virtualization effectively, several different approaches are available. These methods are often used simultaneously and combined within modern virtualization platforms. The chosen approach depends on guest OS support, available hardware features, and the specific configuration settings.
- Software Virtualization Software virtualization does not require special hardware support. Memory protection mechanisms are used to prevent conflicts caused by overlapping access. I/O requests to physical devices are intercepted and forwarded to the hardware by the host software. In this type of server virtualization, the hypervisor emulates devices by analyzing operating system code.
- Hardware Virtualization Hardware virtualization relies on specialized CPU instruction sets or I/O device features, which must be supported by the underlying hardware. Virtual machines can then use hypervisor calls to access devices directly. This increases hypervisor efficiency, as fewer resources are required for emulation.
- Paravirtualization Paravirtualization uses drivers that are specifically adapted to the hypervisor, reducing or eliminating the need for dedicated hardware support. I/O requests are sent directly to the hypervisor at a logical level, which then forwards them to the hardware. This removes the need to monitor guest operating system code and significantly improves communication efficiency between guests and the hypervisor.
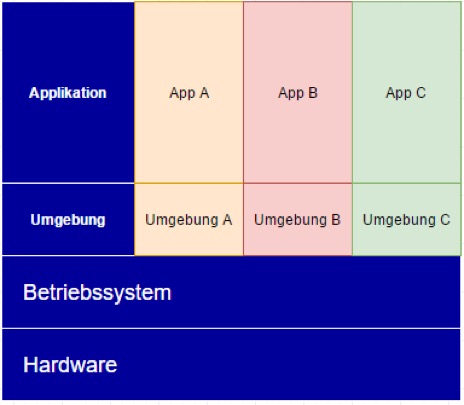
Operating System–Level Server Virtualization
With operating system–level virtualization, only a single operating system is installed on the server. The OS then provides multiple isolated environments. These environments behave like independent operating systems, but they do not have direct access to the physical server. Applications can still be configured and operated independently, ensuring isolation and protection. In this virtualization model, all instances share the same kernel and drivers, which also means a consistent patch level across environments. Depending on the solution in use, the TCP/IP stack may be shared or configured individually.
Server Virtualization: How Virtualization Software Works
In any virtualization environment, the virtualization software plays a central role. Put simply, virtualization platforms—also known as hypervisors—abstract the physical server hardware. Selected server resources are then provided to a guest operating system as virtualized hardware within a virtual machine.
This approach allows multiple servers or clients to be consolidated on shared hardware. As a result, operating costs are reduced through improved resource utilization, simplified administration, and more efficient backup processes. Another key advantage of server virtualization is increased availability for both servers and critical services.
Server Virtualization and the Importance of Hypervisors
When it comes to the type of virtualization, a basic distinction is made between type 1 (bare-metal hypervisor) and type 2 (hosted hypervisor) virtualization concepts. While bare-metal hypervisors are based directly on the hardware and do not require a host operating system, type 2 hypervisors are software that can be installed under Windows, Linux, or MacOS X.
In addition to server virtualization, the software also enables desktop virtualization for virtual desktops or applications. Furthermore, a hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) can be used, which combines servers, storage and networks in an integrated platform.
In practice, however, the limits of this definition are becoming increasingly blurred. For example, Microsoft Hyper-V is considered a bare-metal virtualization product, while KVM (Kernel Virtual Machine, Linux) is a hosted hypervisor.
Everything you need to know about server virtualization and much more at HAPPYWARE
If you are looking for more information on server virtualization or you have further questions, please phone or send us an email - we will be happy to help.


















